フィンランドのトゥルク大学の研究者は、[{” attribute=””>black hole in a binary system is tilted more than 40 degrees relative to the axis of stellar orbit. The finding challenges current theoretical models of black hole formation.
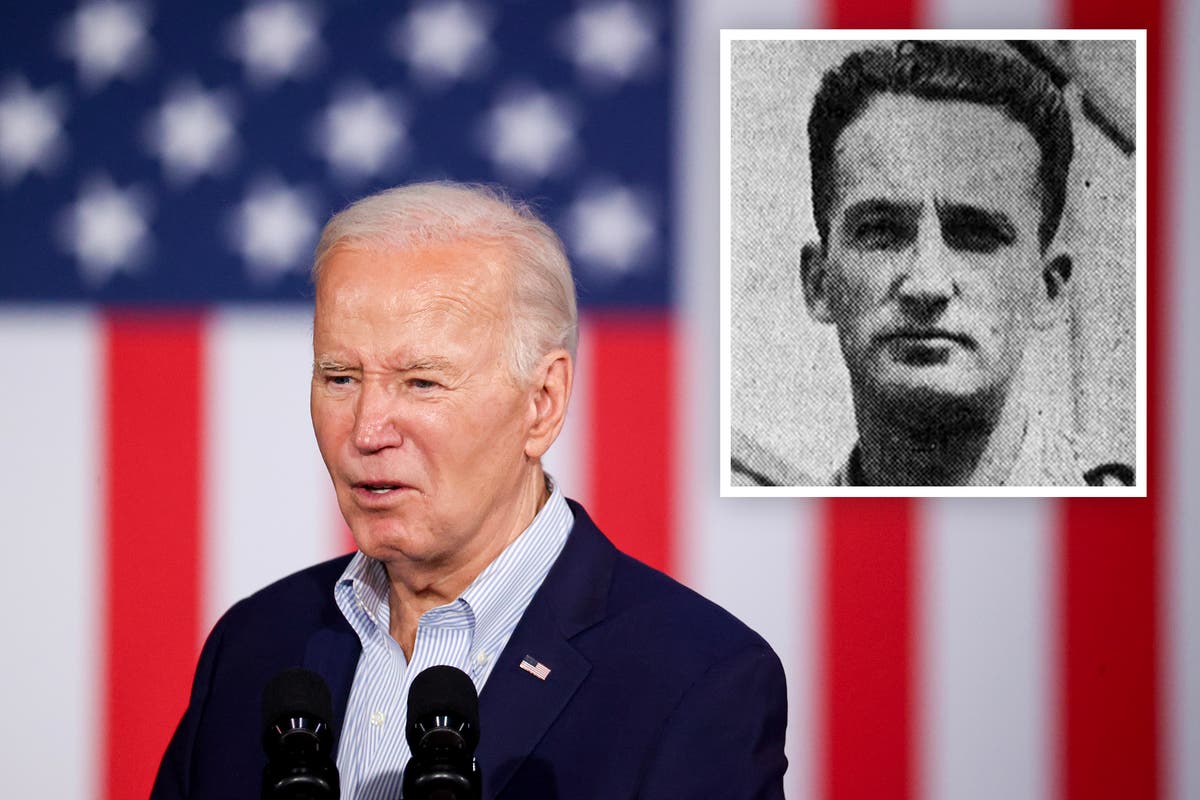
The observation by the researchers from Tuorla Observatory in Finland is the first reliable measurement that shows a large difference between the axis of rotation of a black hole and the axis of a binary system orbit. The difference between the axes measured by the researchers in a binary star system called MAXI J1820+070 was more than 40 degrees.
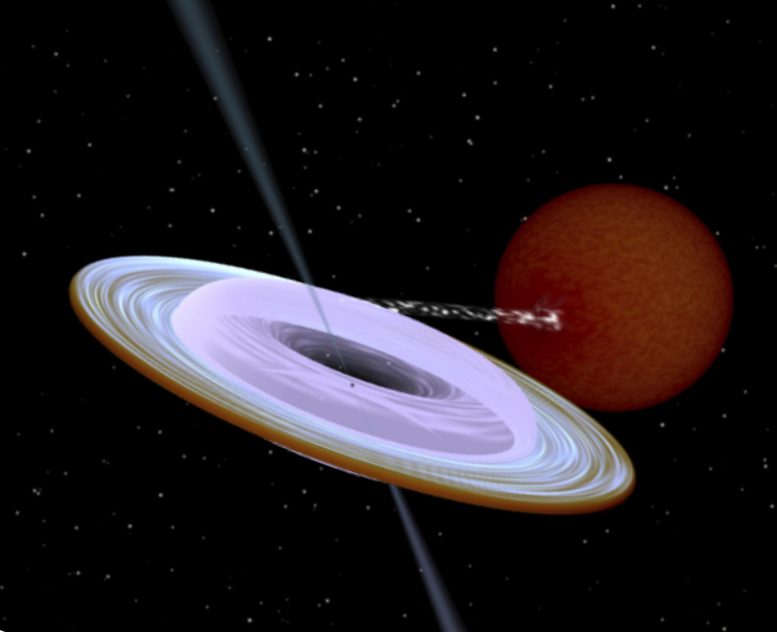

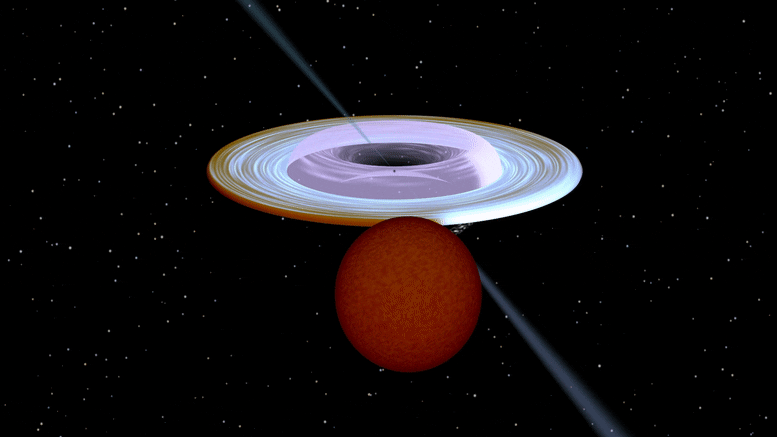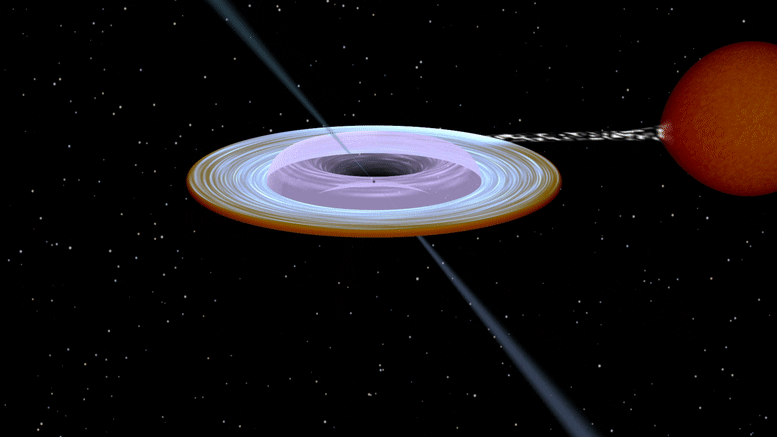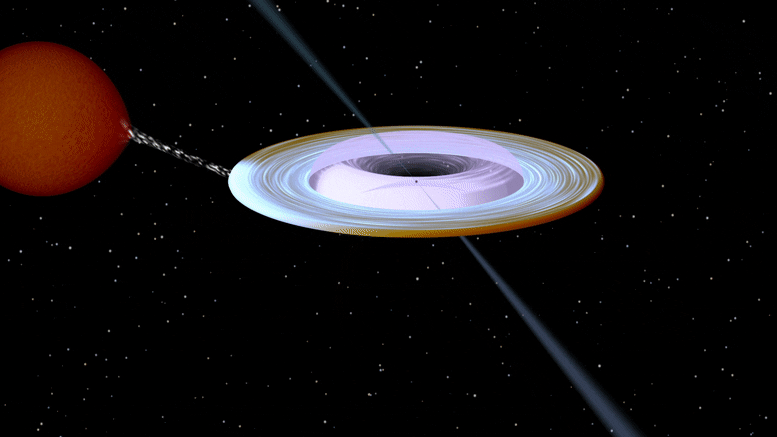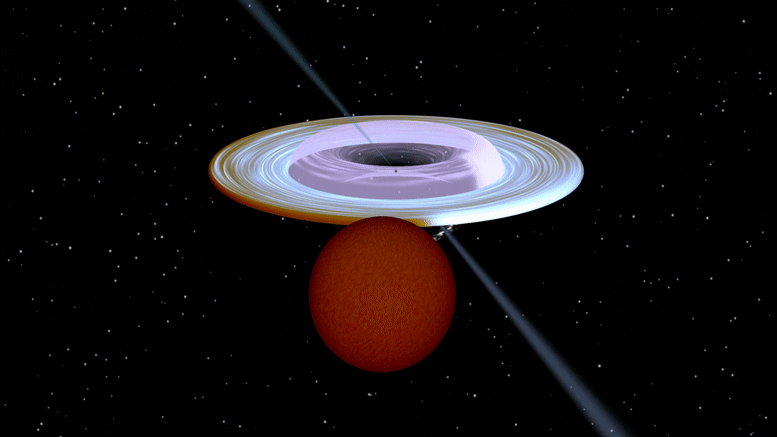
Artist impression of the X-ray binary system MAXI J1820+070 containing a black hole (small black dot at the center of the gaseous disk) and a companion star. A narrow jet is directed along the black hole spin axis, which is strongly misaligned from the rotation axis of the orbit. Image produced with Binsim. Credit: R. Hynes
Often for the space systems with smaller objects orbiting around the central massive body, the own rotation axis of this body is to a high degree aligned with the rotation axis of its satellites. This is true also for our solar system: the planets orbit around the Sun in a plane, which roughly coincides with the equatorial plane of the Sun. The inclination of the Sun rotation axis with respect to orbital axis of the Earth is only seven degrees.
“The expectation of alignment, to a large degree, does not hold for the bizarre objects such as black hole X-ray binaries. The black holes in these systems were formed as a result of a cosmic cataclysm – the collapse of a massive star. Now we see the black hole dragging matter from the nearby, lighter companion star orbiting around it. We see bright optical and X-ray radiation as the last sigh of the infalling material, and also radio emission from the relativistic jets expelled from the system,” says Juri Poutanen, Professor of Astronomy at the University of Turku and the lead author of the publication.
ブラックホール(ガス状円盤の中心にある小さな黒い点)とコンパニオンスターを含むX線連星システムMAXI J1820 +070のアーティストの印象。 狭いジェットはブラックホールの回転軸に沿って向けられ、それは軌道の回転軸から強く歪んでいます。 写真はそよ風で制作されました。 クレジット:R。Hynes
これらのジェットを追跡することにより、研究者はブラックホールの回転軸の方向を非常に正確に決定することができました。 その後、コンパニオンスターからブラックホールに落下するガスの量が減少し始めると、システムの温度が下がり、システム内の光の大部分がコンパニオンスターから来ました。 このようにして、研究者たちは分光技術を使用して軌道傾斜角を測定することができ、これは弾道学の傾斜角とほぼ一致しました。
「軌道の3D方向を決定するには、空のシステムの位置角、つまり、システムが空の北の方向に対してどのように回転するかを知る必要もあります。これは、偏光測定技術を使用して測定されました」と述べています。ジュリポタニン。
科学で発表された結果は、ブラックホールの形成とそのようなシステムの進化の研究に向けて興味深い展望を開きます。なぜなら、ブラックホールの形成とバイナリ進化の多くのシナリオでそのような極端な不均衡を得るのは難しいからです。
軌道軸とブラックホールの回転の40度以上の違いは全く予想外でした。 科学者は、ブラックホールの周りの湾曲した時空での物質の振る舞いをモデル化したときに、この違いは非常に小さいと考えることがよくありました。 既存のモデルはすでに複雑であり、現在、新しい発見により、モデルに新しい次元を追加する必要があります」とポタニンは言います。
参照:Guri Potanin、Alexandra Veledina、Andrei V Berdyugina、Svetlana V Berdyugina、Helen Germak、Peter J. Juncker、Gary JE Kagava、IlyaKozenkovによる「X線連星MAXIJ1820 +070の軌道軌道ブラックホール回転不均衡」 Vadim Kravtsov Filippo Perola、Manisha Shrestha、Manuel A. Perez-Torres、およびSergeS。 ツィガンコフ、2022年2月24日ここで入手可能。 知るために。
DOI:10.1126 / science.abl4679
主な発見は、トゥルク大学と共同所有の北光学望遠鏡に設置された自社製のDIPol-UF偏光計を使用して行われました。 オーフス大学 デンマークで。

「音楽マニア。プロの問題解決者。読者。受賞歴のあるテレビ忍者。」





More Stories
世界保健機関は、鳥インフルエンザが人に伝染するリスクが「大きな懸念事項」であると述べている。 鳥インフルエンザ
巨大な古代の海洋爬虫類がアマチュアの化石発見によって特定された
研究によると、伝統的な日本の食事は女性の脳の健康に有益である可能性があります