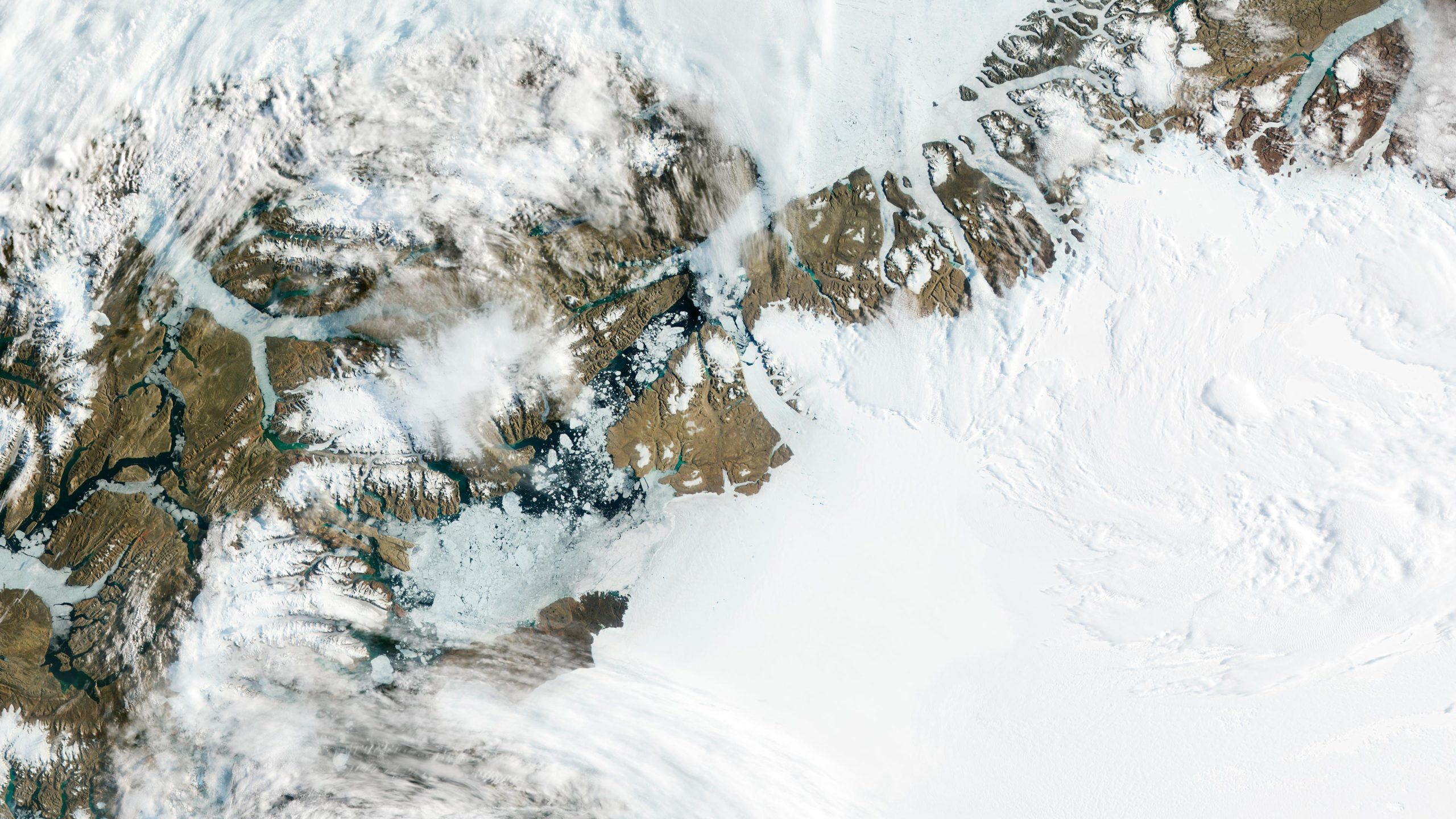
NASA が 2012 年に撮影したこの画像の中心では、グリーンランド北西部のピーターマン氷河が徐々に海に向かって移動しており、その大部分が氷山として切り離され、漂流しています。 UCI と NASA JPL の研究者は、ヨーロッパの 3 つのミッションからの衛星データを使用して、温暖な海水が氷河の地表線を移動させ、急速な衰退につながっていることを確認しました。 クレジット: NASA
この研究は、将来の海面上昇の程度が大幅に過小評価される可能性があることを示唆しています。
新しい研究は、グリーンランドのピーターマン氷河のベースラインが潮汐サイクル中にシフトし、暖かい海水が氷の融解を加速させることを発見しました. この未知の相互作用は、モデルに含まれている場合、海洋を終結させる氷河の海面上昇予測を 200% 増加させる可能性があります。
カリフォルニア大学アーバイン校と NASA のジェット推進研究所の研究者は、グリーンランド北西部のピーターマン氷河で調査を行っているときに、氷と海が相互作用するこれまでにない方法を発見しました。 氷河学者は、彼らの調査結果は、極地の氷の劣化によって引き起こされる将来の海面上昇を気候関係者が大幅に過小評価していることを意味する可能性があると述べた.
ヨーロッパの 3 つのミッション、UCI/[{” attribute=””>NASA team learned that Petermann Glacier’s grounding line – where ice detaches from the land bed and begins floating in the ocean – shifts substantially during tidal cycles, allowing warm seawater to intrude and melt ice at an accelerated rate. The group’s results are the subject of a paper published on May 8 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Petermann’s grounding line could be more accurately described as a grounding zone, because it migrates between 2 and 6 kilometers as tides come in and out,” said lead author Enrico Ciraci, UCI assistant specialist in Earth system science and NASA postdoctoral fellow. “This is an order of magnitude larger than expected for grounding lines on a rigid bed.”
He said the traditional view of grounding lines beneath ocean-reaching glaciers was that they did not migrate during tidal cycles, nor did they experience ice melt. But the new study replaces that thinking with knowledge that warm ocean water intrudes beneath the ice through preexisting subglacial channels, with the highest melt rates occurring at the grounding zone.
The researchers found that as Petermann Glacier’s grounding line retreated nearly 4 kilometers – 2½ miles – between 2016 and 2022, warm water carved a 670-foot-tall cavity in the underside of the glacier, and that abscess remained there for all of 2022.
“These ice-ocean interactions make the glaciers more sensitive to ocean warming,” said senior co-author Eric Rignot, UCI professor of Earth system science and NASA JPL research scientist. “These dynamics are not included in models, and if we were to include them, it would increase projections of sea level rise by up to 200 percent – not just for Petermann but for all glaciers ending in the ocean, which is most of northern Greenland and all of Antarctica.”
The Greenland ice sheet has lost billions of tons of ice to the ocean in the past few decades, the PNAS paper stresses, with most of the loss caused by warming of subsurface ocean waters, a product of Earth’s changing climate. Exposure to ocean water melts the ice vigorously at the glacier front and erodes resistance to the movement of glaciers over the ground, causing the ice to slide more quickly to the sea, according to Rignot.
Reference: “Melt rates in the kilometer-size grounding zone of Petermann Glacier, Greenland, before and during a retreat” by Enrico Ciracì, Eric Rignot, Bernd Scheuchl, Valentyn Tolpekin, Michael Wollersheim, Lu An, Pietro Milillo, Jose-Luis Bueso-Bello, Paola Rizzoli and Luigi Dini, 8 May 2023, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2220924120
Ciraci’s research was supported by the NASA Postdoctoral Program at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Joining Ciraci and Rignot on the project were Bernd Scheuchl, UCI associate project scientist; Valentyn Tolpekin and Michael Wollersheim of Finland’s Iceye mission; Lu An of China’s Tongji University; Pietro Milillo of the University of Houston; Jose-Luis Bueso-Bello of the German Aerospace Center; and Luigi Dini of the Italian Space Agency.

「音楽マニア。プロの問題解決者。読者。受賞歴のあるテレビ忍者。」


More Stories
JGB Curveは、日本の金融の健康に関する懸念の中で認めています – TradingViewニュース
週末の睡眠を補うことで心臓病のリスクが5分の1減少する可能性がある――研究 |心臓病
化石によると、先史時代のカイギュウはワニとサメに食べられた